-
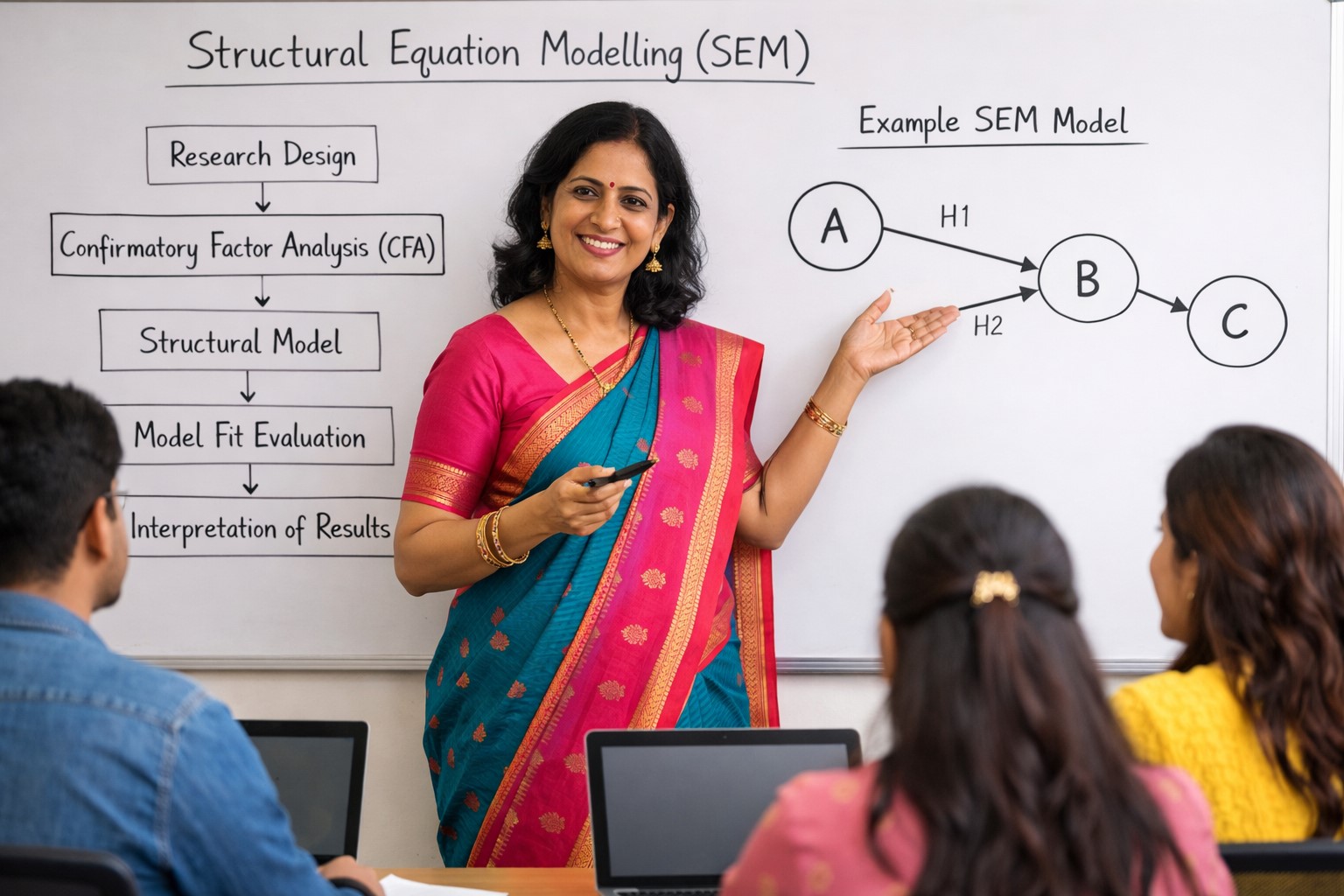
Role of Structural Equation Model in Research
1. Introduction Research in the social sciences, management, education, health, and technology increasingly deals with abstract constructs and complex causal relationships. Variables such as attitudes, perceptions, commitment, satisfaction, and behavioural intentions cannot be measured directly and often interact in intricate…
-
Referencing and Citation in Research
1. Introduction Referencing and citation form the foundation of academic and professional writing. They acknowledge the intellectual contributions of previous scholars, provide credibility to arguments, and allow readers to verify the sources used in a study. Whether a researcher is…
-
Chapterisation of the Thesis in Social Science Research
Introduction Doctoral research in social sciences requires not only originality and methodological rigour but also a clear and systematic presentation of ideas. One of the most important elements that ensures this clarity is the chapterisation of the thesis. Chapterisation refers…
-
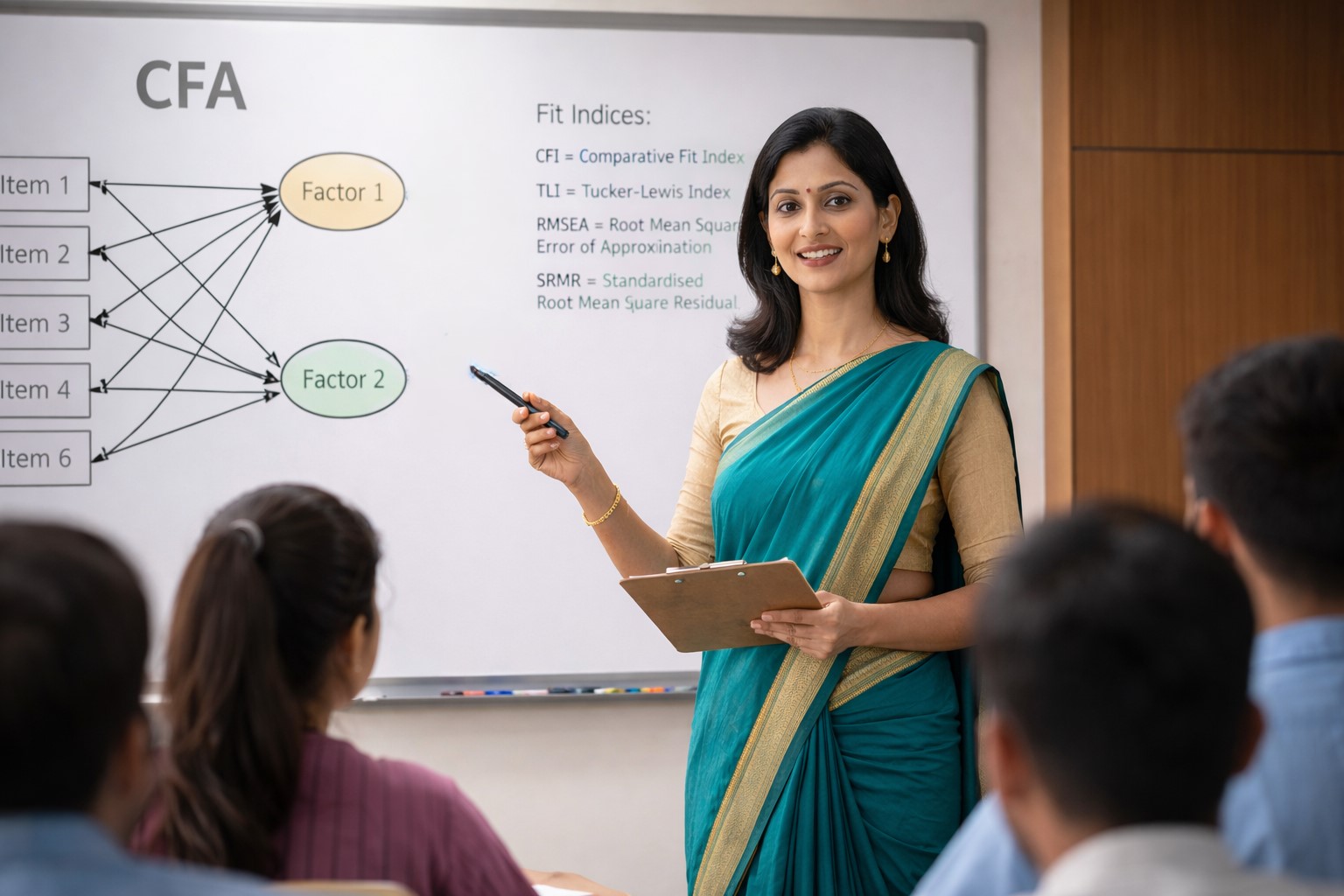
Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) and its usage in Research
Introduction In empirical research, especially within the social sciences, management studies, psychology, education, and health sciences, researchers often deal with abstract concepts such as satisfaction, attitude, intelligence, leadership, trust, or well-being. These concepts cannot be measured directly; instead, they are…
-
Role of Control vs Experimental Groups in Research
Introduction Research aims to generate reliable and valid knowledge by examining cause-and-effect relationships. Whether the study belongs to medicine, education, psychology, business, or social sciences, researchers often need to determine whether a specific factor genuinely influences an outcome. To achieve…
-
Ethics in Research
Introduction Ethics in research refers to the moral principles and professional standards that guide researchers in the planning, execution, analysis, and dissemination of studies. Ethical research ensures that knowledge is generated responsibly, participants are treated with dignity, data are handled…
-
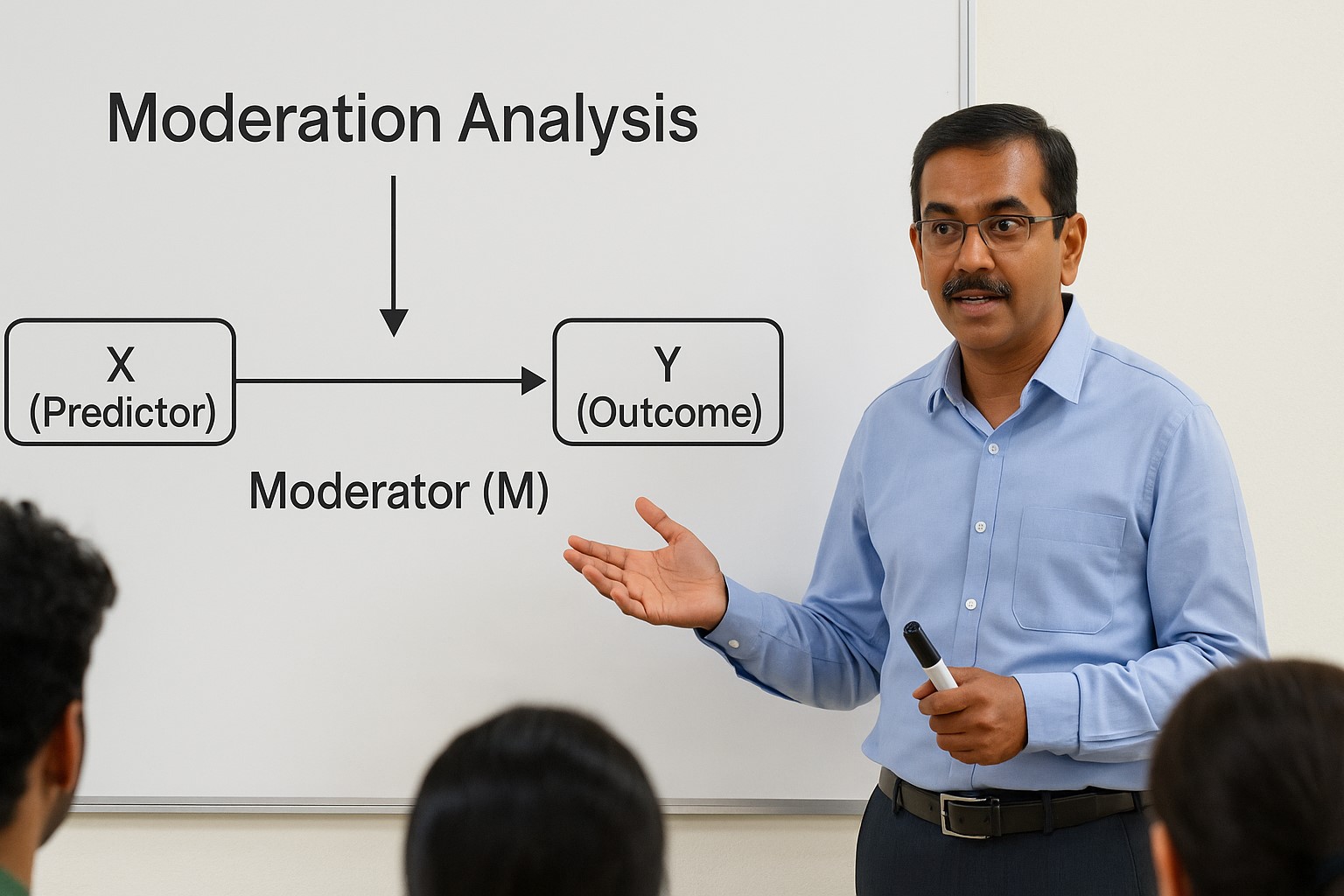
Understanding Moderation Analysis: A Practical Guide with Real-World Examples
In many research settings, relationships between variables do not operate uniformly across all individuals or situations. A factor that significantly influences an outcome in one context may have a different impact when conditions change. Moderation analysis is a statistical approach…
-
NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING IN RESEARCH
Introduction Non-probability sampling plays an important role in research when it is not feasible, practical, or necessary to select participants using statistical probability. Unlike probability sampling, where every unit has a known and equal chance of selection, non-probability sampling relies…
-
Confounding Variables and their Role and Management in Research
Understanding human behaviour, health outcomes, market responses, or environmental changes requires careful research. However, even the most carefully designed studies can go wrong if something outside the main variables quietly influences the results. These “hidden influencers” are known as confounding…
-
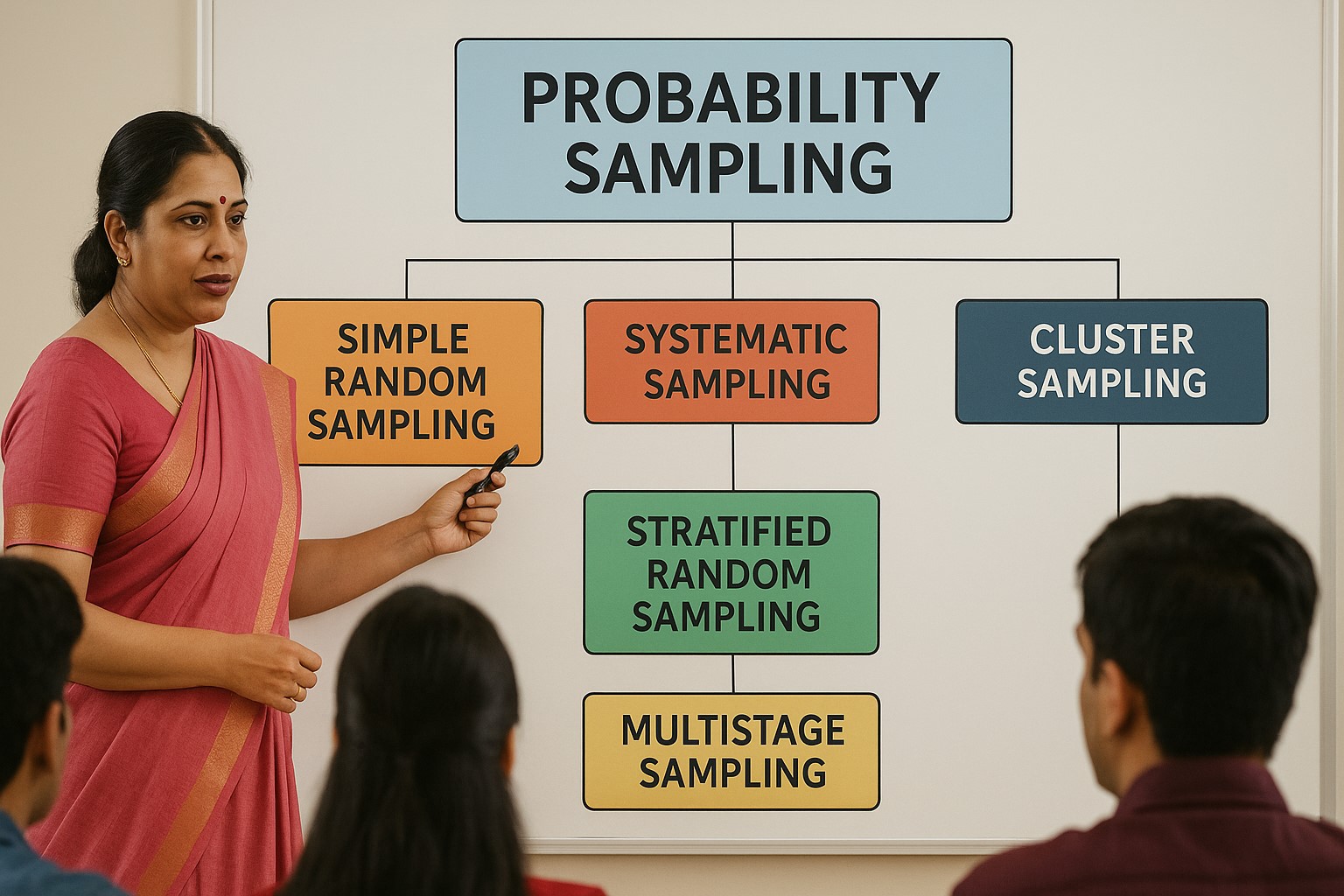
Understanding Probability Sampling
Sampling is one of the most essential steps in any research process. Whether the goal is to understand public opinion, analyse the effectiveness of a medical treatment, or study consumer behaviour, selecting the right sample is central to producing reliable…
Author

Dr. D. Sampath Kumar
Latest Posts
Tags
Chi-Square Test of Goodness of Fit Conceptual Framework Cross-Sectional Design Data Analysis Data Collection Descriptive Design Descriptive Statistical Analysis Distribution-Free Test Ethics in Research Expected frequency Experimental Design Feasibility Goodness of Fit Highly Correlated Literature Review Longitudinal Design Mixed Modification of Scale Multi-Variate Analysis Multicollinearity Test New Scale Development Non-Parametric Tests Non-Probability Sampling Original Scale Parametric Tests Pilot Study Primary Data Probability Sampling Qualitative Quantitative Questionnaire Reliability Research Approach Research Design Research Ethics Research Gap Research Objectives Review of Literature Sampling Sampling Frame Scale Development Secondary Data Survey Theoretical Framework Validity