Introduction
Research plays a crucial role in addressing various socio-economic and business challenges. Whether in technology, healthcare, finance, or environmental sustainability, researchers must ensure that their work is impactful and leads to practical solutions.
Research begins with identifying a problem that needs to be solved. A well-defined research problem sets the foundation for meaningful study and contributes to the existing body of knowledge. Choosing the right research problem requires a thorough understanding of existing literature, industry challenges, and emerging trends. A good research problem should be relevant, feasible, and contribute to academic or practical advancements.
This blog explains how to identify and formulate a research problem with practical examples.
Sources of Identifying a Research Problem
Before selecting a research problem, researchers can explore multiple sources to identify key issues that require investigation:
- Existing Literature – Reviewing academic journals, conference proceedings, and books helps identify gaps in research.
- Industry Trends and Reports – Studying business reports, government publications, and white papers provides insights into emerging issues.
- Practical Challenges – Observing real-world problems faced by businesses, consumers, or policymakers can inspire research topics.
- Expert Opinions – Engaging with professionals, academics, and industry leaders helps understand critical research needs.
- Policy and Regulations – Analysing government policies, legal frameworks, and regulatory changes can reveal unexplored research areas.
Follow the steps given below to identify and formulate the research problem of a research:
Step 1: Identify a Broad Area and Conduct a Literature Review
Start by selecting a broad topic based on your academic background, industry trends, or societal issues. If you are from the field of Commerce, you can choose from domains or broad area of research such as:
- Marketing (e.g., impact of influencer marketing on consumer behaviour)
- Human Resource Management (HRM) (e.g., employee retention strategies in IT companies)
- Finance (e.g., impact of financial literacy on investment decisions)
- Entrepreneurship (e.g., role of government policies in fostering start-up growth)
- International Business (e.g., challenges faced by Indian exporters in global markets)
Conduct a preliminary literature review by checking journals, government reports, and industry publications to understand research gaps with respect to those broad area and also identify the sub-domains.
Some examples of Sub-domains include:
- Sustainable Development (e.g., impact of renewable energy policies)
- Fintech Services (e.g., adoption of UPI payments in rural areas)
- Consumer Behaviour (e.g., online shopping preferences in tier-2 cities)
- Healthcare (e.g., accessibility of telemedicine services in rural areas)
Step 2: Narrow down the Problem and Define it clearly
Define a specific issue within the broad area. Ask questions like:
- What specific aspect is unexplored?
- Who is affected by this problem?
- What practical relevance does it have?
A research problem should be clear, specific, and researchable. It should address a gap in knowledge or a practical issue.
Examples:
What specific aspect is unexplored?
- In digital advertising, while there are studies on consumer engagement, little research has explored how regional language ads impact trust and brand loyalty in India.
- In financial literacy, many studies focus on urban populations, but there is limited research on how financial awareness influences investment decisions among rural women in Tamil Nadu.
Who is affected by this problem?
- Small businesses that want to use regional language advertisements effectively but lack data on consumer response.
- Rural investors who may not have access to adequate financial education and, therefore, make uninformed investment decisions.
What practical relevance does it have?
- Understanding the effectiveness of regional language digital ads can help brands design better marketing strategies to engage local audiences.
- Insights into financial literacy in rural areas can help policymakers and banks create better awareness programs to promote informed investment behaviour.
Research Topic:
Instead of studying digital advertising in general, your research topic should focus on particular/specific issue. The research topic is:
“Effectiveness of Regional Language Digital Ads in driving Purchase Decisions among consumers in Kochi, Kerala.”
Example Problem Statement:
“Despite the rapid growth of digital advertising in India, there is limited research on how regional language ads impact consumer trust and purchase behaviour. This study aims to investigate the effectiveness of Malayalam-language digital ads in influencing online shopping preferences in Kochi, Kerala.”
Step 3: Formulate Research Objectives and Questions
After defining the problem, outline research objectives to guide your study and convert them into research questions.
Example Objectives:
- To analyze consumer perception of regional language advertisements.
- To examine the impact of Malayalam-language ads on purchase decisions.
- To compare engagement levels between English and Malayalam digital ads.
Example Questions:
- How do consumers perceive regional language digital advertisements?
- Do Malayalam-language ads create higher engagement compared to English ads?
- What factors influence trust in regional language digital advertisements?
Step 4: Justify the Research Problem
Explain why this problem matters. Justification can be based on:
- Societal Impact: Helps businesses tailor advertising strategies for regional markets.
- Academic Contribution: Fills the research gap on regional digital marketing.
- Business Relevance: Assists brands in improving consumer engagement through localized ads.
Step 5: Develop a Research Framework and Conclusion
Develop a framework that outlines the study approach, including methodology, target audience, and expected outcomes. A well-defined problem ensures clarity in research direction and contributes valuable insights to academia and industry.
The following practical examples of two difference fields of study explain in detail about the steps to identify and formulate the research problem:
PRACTICAL EXAMPLE 1: (MANAGEMENT/COMMERCE)
Step 1: Identify a Broad Area and Conduct a Literature Review
Broad Area/Domain: Human Resource Management (HRM)
Sub-domain/Sub-area: Organisational Behaviour or Performance Management
Specific Issue: Remote work policies in the Indian IT sector.
Literature Review Insights:
Existing research covers work-life balance and employee motivation, but limited studies analyze the long-term impact of remote work on job satisfaction and productivity in India’s IT industry.
Step 2: Narrow Down the Problem and Define it clearly
Unexplored Aspect: The effectiveness of hybrid work models on employee productivity and job satisfaction.
Who is Affected?: IT employees, HR managers, and organizations implementing remote work policies.
Practical Relevance: Helps IT companies refine work-from-home policies for improved efficiency and employee well-being.
Research Topic:
“Impact of Work-from-Home Policies on Employee Productivity and Job Satisfaction in Indian IT Companies with reference to Chennai”
“Despite the rise in remote work adoption in Indian IT firms, there is limited research on how hybrid work models impact employee productivity and job satisfaction. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of work-from-home policies and identify key factors influencing employee engagement.”
Step 3: Formulate Research Objectives and Questions
Objectives:
- To examine the impact of work-from-home policies on employee productivity.
- To assess employee job satisfaction in hybrid and fully remote models.
- To explore challenges faced by employees and HR managers in remote settings.
Research Questions:
- How do work-from-home policies influence employee productivity?
- What factors contribute to job satisfaction in remote work setups?
- What are the HR challenges in managing remote employees in the IT sector?
Step 4: Justify the Research Problem
Societal Impact: Helps improve work-life balance and job satisfaction for employees.
Academic Contribution: Adds insights to HRM literature on remote work effectiveness.
Business Relevance: Provides recommendations for IT firms to optimize work-from-home policies.
Step 5: Develop a Research Framework and Conclusion
The study will use employee surveys, HR policy analysis, and productivity metrics to evaluate remote work effectiveness. It will contribute to HRM strategies in the IT sector.
PRACTICAL EXAMPLE 2: ECONOMICS
Step 1: Identify a Broad Area and Conduct a Literature Review
Broad Area/Domain: Economics
Sub-Domain: Monetary Economics
Specific Issue: Financial inclusion and digital payments in India.
Literature Review Insights: Research exists on UPI and digital payment adoption in urban areas, but limited studies focus on their impact on rural financial inclusion.
Step 2: Narrow Down the Problem and define it clearly
Unexplored Aspect: The effectiveness of government-led digital payment initiatives (e.g., UPI, Aadhaar-linked banking) in improving rural financial inclusion.
Who is Affected?: Rural consumers, Small businesses, and Policymakers.
Practical Relevance: Insights will help the government and financial institutions improve digital payment accessibility in rural India.
Research Topic:
“Impact of Government Digital Payment Initiatives on Financial Inclusion in Rural India with special reference to Nellore District, Andhra Pradesh”
“Despite the rapid adoption of digital payment platforms in India, financial inclusion in rural areas remains a challenge. This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of government digital payment initiatives in enhancing rural financial access and participation.”
Step 3: Formulate Research Objectives and Questions
Objectives:
- To assess rural awareness and adoption of digital payment methods.
- To analyze challenges faced by rural consumers in using digital payments.
- To evaluate the impact of digital financial initiatives on financial inclusion.
Research Questions:
- How effective are government digital payment initiatives in increasing financial inclusion in rural India?
- What are the barriers to adopting digital payments in rural areas?
- How does digital literacy affect rural consumers’ usage of digital payment systems?
Step 4: Justify the Research Problem
Societal Impact: Helps bridge the financial gap between rural and urban populations.
Academic Contribution: Adds to the discussion on digital banking and rural financial policies.
Business Relevance: Assists fintech companies and policymakers in improving digital financial services.
Step 5: Develop a Research Framework and Conclusion
The study will use survey data from rural households, analyze digital transaction trends, and assess policy effectiveness in promoting digital financial inclusion. Findings will help enhance financial accessibility in India’s rural regions.
Here is a table incorporating the five steps with examples from three different fields of study/domains, namely, Computer Science, Environmental Science and Psychology and helps you in identification and formulation of Research Problem.
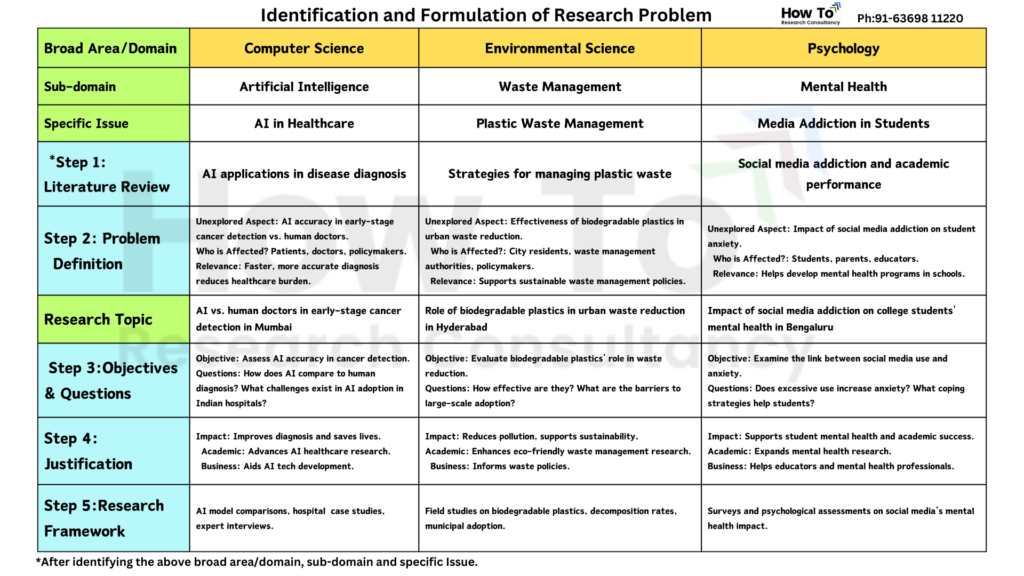
Conclusion
Identifying and formulating a research problem is the first step in conducting meaningful research. A well-defined research problem ensures that the study remains focused, relevant, and valuable to academic and practical domains. By carefully selecting a research area, conducting a literature review, and refining the problem statement, researchers can contribute to knowledge and provide solutions to real-world challenges.
By applying these principles with practical examples, researchers can develop relevant studies that address local challenges and global trends effectively.
Call to Action
Struggling to identify and formulate your research problem? Need expert guidance?
Share your research domain in the comments or reach out to us for personalized advice to refine your research problem and enhance the depth of your study!









Leave a Reply